Prostate Cancer Treatment Los Angeles
Best Prostate Cancer Doctors in Los Angeles, CA.

Prostate Cancer Treatment and Clinical Trials
Prostate cancer is second most common cancer in men, with 1 in 7 men projected to be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. Having a board-certified urologist on your side is essential to restoring your health and recovering your sexual function.
At Comprehensive Urology in Beverly Hills, Los Angeles, we specialize i diagnosis the symptoms of prostate cancer and providing prostate cancer treatment in our state-of-the-art facilities. Dr. Kia Michel and his expert team work tirelessly to optimize your outcomes and provide the best solutions available. To get screened for prostate cancer, schedule an appointment with Comprehensive Urology. You can book by phone or book online today.
Table of Contents
What is Prostate Cancer?
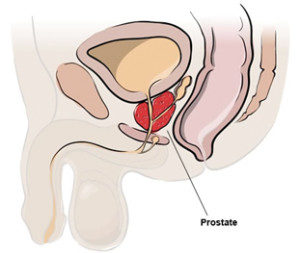
Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland. This is a walnut-shaped gland located in the male lower abdomen. Its function is to produce fluid for transporting and nourishing sperm. Early detection and treatment is the best way to fight prostate cancer and prevent it from spreading to other parts of your body.
An important point to note is prostate cancer begins to grow in the prostate gland. If left untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body and progress into advanced prostate cancer. Facing a prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but understanding the available treatment options can provide a sense of empowerment and guide you towards making informed decisions. In this blog, we delve into the various treatment options for prostate cancer, exploring surgical interventions, radiation therapy approaches, hormone therapy, and the latest advances in Focal Therapy. By gaining knowledge about the benefits, potential side effects, and considerations for each treatment, you can navigate your prostate cancer journey with confidence and take an active role in your treatment plan.
Prostate Cancer is diagnosed using a combination of PSA bloodwork, a physical exam, a medical history of your prostate cancer symptoms, and an MRI Fusion Prostate Biopsy.
Many Men are hesitant to be evaluated for prostate cancer symptoms because they’re often more afraid of the side effects of prostate cancer treatment than they are of the cancer itself. However, our staff has had great results using Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction both before and after prostate cancer treatment. We also offer state of the art therapies that minimize the side effect of prostate cancer. With us, you have options that you wouldn’t find anywhere else as we host many new studies at our Beverly Hills facility.
What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
You may not experience any symptoms of prostate cancer, especially in its early stages. One of the most common symptoms in the earliest stages of the disease is a change in urination and difficulty holding in your urine.
More advanced prostate cancer can cause:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Bone pain
- Pelvis Pain or Pain in your Lower back
- Blood in your semen
- Difficulty urinating
- Decreased urine stream force
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, you should book an appointment with your urologist. Getting screened for prostate cancer helps your urologist detect the disease before symptoms occur. In general, most men should have a screening every 2-3 years however, this timeline can vary. Your screening plan will depend on your risk factors, previous results, and your medical history.
Prostate Location: Where is the Prostate Located?
The prostate is a gland in the reproductive system. It’s located above the perineum (the space between the anus and scrotum) and below the bladder, . It measures about the size of a walnut and covers the area around the urethra, which dispenses urine in the bladder. The prostate produces seminal fluid, which protects and transports sperm.
What causes Prostate Cancer?
Unfortunately, it’s not yet known what causes prostate cancer to develop. Doctors do, however, know how it develops.
The initiation of prostate cancer originates from DNA. DNA is present in the cells throughout the body and serves as the blueprint for generating new cells. Occasionally, cellular DNA undergoes corruption, resulting in an alteration of the blueprint. This modified blueprint directs cells to proliferate and divide at a rate exceeding their normal parameters.
Additionally, healthy cells have a life cycle in which they are created, grow, and then die. But the new, abnormal cells – the cancer – continues living, growing, and spreading instead of dying. Because they don’t die naturally, the abnormal cells collect and form tumors which may spread and invade other parts of the body.
While doctors don’t yet know what causes the DNA to be altered, there are several factors that can increase your risk of developing prostate cancer. These include:
Age: Your risk of prostate cancer increases as you age. It’s most common after age 50.
Race: For unknown reasons, Black people have a greater risk of prostate cancer than do people of other races. In Black people, prostate cancer is also more likely to be aggressive or advanced.
Family history: Your risk of developing prostate cancer is increased if a blood relative, such as a parent, sibling or child, has been diagnosed with either prostate cancer or breast cancer.
What are the Stages of Prostate Cancer?
Once you have undergone screening to detect prostate cancer, your doctor will review the results and create a treatment plan for you. The treatment plan will be created with the stage of your prostate cancer in mind. These stages include:
Stage 1
In the first stage, the cancer is present in such a small area of the prostate, that it’s undetectable during a rectal exam. A biopsy or surgery for a prostate-related issue can detect the cancer cells.
Stage 2
The cancer has spread to a larger area of the prostate and typically both lobes of the prostate gland. The cancer hasn’t spread outside of the prostate gland and can be detected during a prostate exam.
Stage 3
During the third stage, prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland to the seminal vesicles and lymph nodes.
Stage 4
This is the most advanced stage of the disease, with the metastatic prostate cancer having spread to other organs including the bladder, rectum, pelvic wall, bones, liver, and brain.
What are the Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer?
While anyone can develop prostate cancer, certain factors increase your risk of experiencing the disease. Statistically vulnerable groups include:
- Older age groups
- African-Americans
- Individuals who struggle with obesity
- Patients with a family history of prostate cancer
Some complications of prostate cancer or its treatments may include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary incontinence
It is vital to have a complete diagnosis before jumping to conclusions. At Comprehensive Urology, we provide expert screenings to evaluate your situation accordingly.
How does my urologist diagnose prostate cancer?
Your urologist will use several methods to find out if you have prostate cancer. They will begin by completing a physical exam and reviewing your medical history and symptoms. Based on this initial review, you may be recommended other procedures to provide a clearer picture.
These options may include the following diagnostic testing procedures:
- Digital rectal exams
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests
- Genetic testing
- Biomarker screening
- High-definition ultrasound
- MRI fusion biopsies
- Multiparametric MRIs
- Targeted and saturation biopsy techniques
- Pre-biopsy PCR testing
What is a PSA Test (Prostate Specific Antigen)?
Comprehensive Urology offers a complete suite of screening options. Each is performed by a highly experienced and respected prostate cancer specialist. These include advanced diagnostic capabilities and prostate mapping that are designed to help you achieve the best outcome possible. We also provide sedation during prostate biopsies to ensure your procedure is comfortable and pain-free.
What are the most common Prostate Cancer Treatment options?
Prostate cancer treatment options can be broken up into 4 categories:
Active Surveillance
Local Treatment for Prostate Cancer
Systemic Treatment for Prostate Cancer
Combination of Prostate Cancer Treatments
What is the best hospital to treat prostate cancer?
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, CA is the top hospital for Prostate Cancer Treatment and has ranked the #1 hospital in California and #2 hospital nationally by U.S. News. It has been nationally ranked in 11 adult specialties with top marks in Prostate Cancer Surgery. Dr. Kia Michel at Comprehensive Urology has hospital privileges at Cedars-Sinai and has been listed by a top urologist on Super Doctors for Southern California for over 20 years.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Q&A
At Comprehensive Urology, we believe in offering a full suite of services with a customized treatment plan that is tailored to the individual needs of our patients. Whenever possible, minimally invasive therapies are used first, while therapies that tend to have more side effects such as surgery are reserved for more advanced prostate cancer cases.
We also focus on providing treatment that is tailored to your situation and needs. The treatment can depend on your symptoms and the status of the cancer itself.
Focal therapy helps preserve erectile function, urinary control, and quality of life. Comprehensive Urology providers follow prostate preservation protocols. Your unique prostate cancer treatment depends on the severity of your condition and might include:
What is Surveillance in Prostate Cancer Treatment
Older men without symptoms of prostate cancer can employ active surveillance, also known as watchful waiting, as a preventive measure against the disease. Through watchful monitoring, healthcare providers closely observe patients and only administer treatment if there are signs or changes in their condition that necessitate intervention. The objective of treatment is to alleviate symptoms and enhance overall health. This approach facilitates the early detection of deteriorating symptoms.
However, with the next generation of prostate cancer treatment options coming to light, such as Focal Therapy (TULSA-Pro), many physicians are trying to reduce the prostate cancer with fewer side effects than more standard treatments. To learn more about active clinical trials, please contact Dr. Kia Michel at Comprehensive Urology in Beverly Hills.
Focal Therapy: Next Generation Prostate Cancer Treatments?
Focal Therapy is a new treatment option for prostate cancer and BPH that either heats or freezes focused areas of the prostate instead of removing the prostate. It is typically used in early-stage prostate cancer treatment (Stage I and II).
The two primary forms of Focal Therapy are TULSA-Pro and HIFU. HIFU uses high-frequency sound waves to destroy cancerous tissue. It has a shorter recovery time than traditional cancer treatments, with less likelihood of side effects. HIFU is performed with a larger device inserted into the anus.
TULSA, on the other hand, uses high-intensity ultrasound waves to heat and destroy cancerous tissue within the prostate while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. TULSA-Pro is performed in an MRI machine with a small device inserted into the urethra.
The TULSA-PRO procedure is a personalized, minimally invasive approach for treatment of both prostate cancer and an enlarged prostate. This allows for customization of the treatment to suit individual situations and improves preservation of sexual and urinary function. The TULSA-PRO can effectively destroy cancerous cells while preserving healthy cells and is carefully planned to minimize the common side effects of prostate surgery, such as loss of bladder control and erectile dysfunction (ED).
Ongoing Clinical trials are confirming their efficacy and side effects compared to the more standard surgery and radiation options. The TACT study showed that TULSA-Pro resulted in a 95%+ reduction in PSA (prostate specific antigen) four years after the treatment, and only a 20% side effect of erectile dysfunction. TULSA-Pro is currently in the CAPTAIN study to see if it is as effective and safe as robotic surgery. Dr. Kia Michel is an investigator in this study, and you can contact Comprehensive Urology today to see if this treatment is right for you. Book an appointment.
What is High-intensity focused ultrasonography (HIFU) for Prostate Cancer?
HIFU is a form of focal therapy that uses high-intensity ultrasound waves to neutralize cancerous prostate tissue. This method is excellent because it works in place of surgery or radiation therapy. The treatment precisely targets cancer within your prostate instead of removing the gland, making it an ideal treatment for many patients.
What is TULSA Procedure for Prostate Cancer?
Also known as TULSA-Pro, the TULSA Procedure is another form of focal therapy that uses thermal ablation to treat prostate cancer. This non-surgical treatment fights the cancer cells while still ensuring the function of the penis and prostate, which can encourage a quicker recovery.
TULSA-Pro typically takes a single session and allows for a flexible, customizable treatment that fits your unique needs. This treatment does not require any incisions or radiation, as MRI treatment is used to kill cancer cells without affecting other organs and non-cancerous tissue. This non-invasive treatment is a suitable choice for many patients.
What is Robotic Surgery for Prostate Cancer Treatment?
One effective method is the robotic da Vinci prostatectomy. This and other robotic surgical procedures help your provider remove cancerous tissue. Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that uses advanced technology for optimal precision and accuracy to remove part of your prostate gland, gallbladder, or cysts. Robotic surgery is often used for a radical prostatectomy, which means that the entire prostate gland is removed and has long been considered a standard treatment for prostate cancer.
This surgery requires smaller incisions, has a shorter recovery time, and has a lower risk of complications when compared to traditional surgery. Robotic surgery typically takes several hours and requires general or regional anesthesia for a painless procedure. After the surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for one to two nights and wear a urinary catheter for 1-2 weeks, depending on the type of surgery performed.
The side effects of a radical prostatectomy are significant, which is why newer therapies are emerging with less side effects, such as TULSA-Pro.
What is Advanced Radiation Therapy?
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses X-rays or other types of energy to kill cancer cells within or near your prostate gland. Since radiation can target specific parts of your body, there are fewer risks of complications from the treatment. This treatment is often used to treat advanced prostate cancer.
There are two types of radiation therapy: external beam radiation therapy and internal beam radiation therapy.
External Beam Radiation Therapy
With external beam radiation therapy, the urologist uses a machine to send radiation waves into your body by penetrating through your skin to kill cancer cells with extreme precision.
Internal Beam Radiation Therapy
During Internal beam radiation therapy, your urologist sends radiation waves into your body by using a wire, tube, or capsule. This method is more precise than external beam radiation therapy and is performed using general anesthetic in hospitals.
The type of radiation therapy best for you will depend on several factors including your age, severity and location of the cancer, your general health, and the size of the tumor. While the amount of sessions required also depends on these factors, both of these radiation therapies take several weeks of treatment.
Other Treatments
Additional solutions for prostate cancer or complications from cancer treatments include:
- Shockwave Therapy (AKA PulseWave therapy)
- Active surveillance
- Hormone Therapy
- Cryotherapy
- Pelvic floor therapy for erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence
A treatment for prostate cancer can either deter growth of prostate cancer cells, like hormone therapy, or can destroy prostate cancer cells in a targeted therapy such as focal therapy. Prostate cancer treated with a variety of targeted therapies is often recommended for the best results.
What is Shockwave Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction during Prostate Cancer Treatment?
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses low-intensity radio waves to speed up tissue repair and increase blood flow to the penis. A specialist places a device near different areas of the penis to emit pulses. These pulses stimulate nerve endings in the penis, which can help increase sensitivity to improve erectile function.
This popular treatment is one many patients choose as it is effective, non-invasive, and has less risk of complications.
The shape and delivery of your treatment can vary. While working with your prostate cancer specialist, you can obtain a plan suited to your situation. Every aspect of treatment is carefully considered before being used. Our goal is to provide you with the most effective treatment available for you.
Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials in Los Angeles
There are many new prostate cancer treatment studies to determine the efficacy and safety of new treatments. At Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles, we offer smaller observational studies and enrollment in larger studies such as the TULSA-Pro CAPTAIN study.
The CAPTAIN Study is currently enrolling patients in Beverly Hills, CA to compare the TULSA-Pro focal therapy vs. the standard treatment of robotic prostatectomy surgery, which consists of removing the entire prostate. Schedule Your Appointment Today to enroll in the TULSA-Pro study or to discuss other prostate cancer treatment options with Dr. Kia Michel. Your health is our top concern, always.
Prostate Preservation
Traditional treatments have typically involved applying radiation to the entire prostate gland, potentially leading to over-treatment. With new advancements in imaging and diagnostic capabilities, Comprehensive Urology can offer some patients targeted treatment through focal prostate cancer therapy. Contact Comprehensive Urology to learn if focal therapy is right for you.
Robotic Surgery
Modern robotic surgery equipment allows for minimally invasive surgery with more accuracy and precision than ever before. The Da Vinci Surgical System, a robotic, computer-guided surgical platform, is changing the face of surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Comprehensive Urology offers patients the most advanced treatment modalities available in the country. Call (310) 278-8330 today to learn more about:
- MRI TrueBeam Therapy
- MRI Brachytherapy
Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer
Age
Prostate cancer is rare in young men, but after age 45 to 50 the risk progressively increases. In the United States, a man has a one in six chance of developing prostate cancer. The cancer is usually slow-growing, and the causes of the disease are multifactorial.
Genetic Link
Men with a son, father or brother with prostate cancer have double the risk of developing the cancer. The risk is even higher for men with several affected relatives, particularly if their relatives were young at the time of diagnosis. Scientists have identified several inherited genes that seem to increase risk, but they probably account for only a small fraction of cases. Genetic testing for these genes is not yet available.
Ethnicity
Ethnic origin also plays a part: men of African heritage seem to be at highest risk, and men of Far Eastern descent the lowest. Men who are at higher risk (family history or African origin) are screened at an earlier age in order to find the cancer at its earliest stages, when the potential for cure is the highest.
Diet
There have been studies linking prostate cancer to a high animal fat and red meat diet. It may be possible to reduce the risk of developing cancer by cutting down on dairy foods, red meats and other foods rich with saturated fats.
Exposure to certain agricultural pesticides may be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. There is also a weak association between prostate cancer and cadmium exposure. Some studies have also linked a previous history of prostate infection to a higher risk of developing cancer.
Grading and Staging
If cancerous cells are found, the pathologist will use a grading system (called Gleason grading) to help describe how aggressive the cancer is. The pathologist will evaluate the two largest areas of cancer and will give each section a grade from 1 (least aggressive) to 5 (most aggressive). When these two numbers are added together, it represents the total Gleason score of the cancer. A higher score signifies a more aggressive cancer. Read more about Prostate Cancer Grading and Staging.
Staging of Prostate Cancer
Our physicians will use clinical information such as:
- the findings noted on the rectal examination,
- the gleason grade of the cancer,
- how much tumor is present in the biopsy specimen,
- how many different areas of the prostate had detectable cancer cells,
- the PSA value, and
- the size of the prostate
…to determine how much cancer is the present, how fast the cancer is growing, and to determine if the cancer is still localized to the prostate (early stage) or if it has spread beyond the prostate (late stage).
Tests Used for Staging Prostate Cancer
Sometimes the physician will order additional diagnostic exams to help determine if the prostate cancer is limited to the prostate or if it has spread. These tests may include a bone scan, CT scan, MRI, and/ or lymph node biopsy. These tests are usually performed when there is a suspicion of aggressive or advanced disease (for example PSA > 10 or bone pain).
Prostate Cancer Treatment by Stage
Treatments for Early Stage Prostate Cancer
Men who are determined to have early stage prostate cancer have a high likelihood that their cancer is still limited to the prostate and has not spread elsewhere. Most men with early stage disease have an excellent prognosis and with current treatment options have a high likelihood of becoming cancer free.
Patients who have early stage disease have several options for treatment including:
- Active Surveillance
- Surgery
- External Radiation Therapy
- Brachytherapy
- Cryotherapy
- Hormonal Therapy
Active Surveillance
Active Surveillance or, as some call it, watchful waiting, may be an option for older men with a relatively shorter life expectancy, especially if the cancer is small and slow growing. Chances are good that without any form of treatment the cancer will not affect them in their lifetime. However, for men who are healthy and have longer life expectancies (greater than 10 years), some type of active treatment to potentially cure the disease is generally recommended
Active surveillance involves monitoring the cancer by:
- Assessing the clinical symptoms of the patient,
- Monitoring his prostate with rectal examinations and PSA testings,
- Imaging the prostate, and
- Repeating the prostate biopsies at regular intervals
Surgery
Recent studies demonstrate that, for patients with early stage disease, surgery affords the best long term cancer control as compared to any other available treatment option. With the development of newer, more advanced surgical instrumentation, patients are able to undergo prostate surgery and achieve excellent cancer control while optimizing their recovery and preservation of function.
Surgery (called Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy) is considered the gold standard and most common treatment for prostate cancer. The surgeon removes the prostate while sparing muscles and nerve fibers surrounding the prostate gland that control erectile function and urination.
Open radical retropubic prostatectomy (the “open” approach) is performed using an incision from the lower abdomen from just below the umbilicus to the pubic bone. The prostate is removed through this incision while sparing the nerves and muscles surrounding it which help to control urination and sexual function. It is the traditional method of prostate removal and sampling of the lymph nodes surrounding the gland where the cancer can potentially spread. The gland is surgically removed, and the surgeon then reconnects the bladder to the urethra to reconnect the urinary tract.
With the advent of newer surgical technology, prostate cancer treatment is now being done in a minimally invasive manner termed the Da vinci prostatectomy (or robot-assisted radical prostatectomy). The benefits of open surgery are maintained (excellent cancer control, preservation of urinary control and erectile function) while using minimally invasive surgical techniques. This results in smaller incisions, less bleeding, less pain, shorter hospitalization and a much faster recovery time. Preliminary data also suggests a more rapid return of urinary control and erectile function with the “robotic” approach.
External Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy can take different forms- either externally beamed from a machine or by radioactive seeds implanted in the prostate (see brachytherapy). It can be used as an alternative to surgery for localized prostate cancer, or to treat cancer that has spread beyond the prostate. In certain clinical situations, radiation treatment can be useful in treating prostate cancer after surgery. Radiation therapy can also help shrink tumors in men with advanced disease, and may also be used to relieve pain caused by prostate cancer.
Radiation therapy has recently been more widely used in conjunction with hormonal therapy in the treatment of more aggressive localized prostate cancer.
The course of external beam radiation therapy is usually 6-8 weeks. Newer therapies are continuously being developed (i.e. Conformal beam radiotherapy, intensity modulated radiotherapy) to improve localization of radiation treatment to the prostate without damaging adjacent structures like the bladder or rectum. Widespread long-term data is awaited to determine durable cure rates compared to other therapies such as radical prostatectomy.
Brachytherapy
Radioactive seed implants are placed into the prostate gland to help localize radiation treatment to the prostate and minimize the effects to the surrounding structures (bladder and rectum). The technique is performed by implantation through the skin utilizing ultrasound and x-ray for localization into the gland. Results published to date show good control of cancer at 5-8 years following treatment in persons with very low grade cancers. Overall, the treatment appears to be as effective as external radiation. Long-term results are awaited in order to determine durable cure rates compared to radical prostatectomy.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is performed by freezing the prostate with liquid nitrogen. In the operating room, small probes are placed by ultrasound guidance into the prostate and then are used to freeze the gland, while the urethra is monitored to minimize the risk of damage to it as well as the rectum. It was first developed in the 1960’s and refined in the early 1990’s but had significant side effects to the urinary tract and rectum. Improved technology and the use of ultrasound has allowed for improved localization of treatment to the prostate gland. The overall cure rate with this technique for primary prostate cancer is yet to be determined due to the short term data that is available.
The therapy has gained more widespread acceptance not in the primary treatment of prostate cancer, but in the recurrence of prostate cancer after radiation treatment has failed. It appears that this may be the more promising role for cryotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer.
Hormonal Therapy
Many men choose hormonal therapy for advanced prostate cancer to help cut off the supply of the hormone (testosterone) that makes prostate cancer cells grow faster. As it is not a curative mode of treatment, it is generally not used in early cancer. Hormonal control can be achieved through the use of medications or through surgical means. The medications used help to stop the production of these hormones or block them from feeding the cancer cells. Surgical options include removal of the testicles, which are the main source of testosterone production in men.
Hormonal therapy targets cancer that has spread beyond the prostate gland and is thus beyond the reach of local treatments such as surgery or radiation therapy. Hormonal therapy is also helpful in alleviating the painful and distressing symptoms of advanced disease. It is also being used in conjunction with external radiation therapy for more aggressive but localized prostate cancer. Furthermore, it is also used as a treatment for prostate cancer recurrence after previous treatment. Although hormonal therapy cannot cure prostate cancer, it will usually shrink or halt the advance of disease, often for years. With hormonal control, about half of men who have the cancer spread to other organs in the pelvis live at least 5 years.
Treatments for Advanced Stage Prostate Cancer
Advanced stage prostate cancer signifies that the cancer cells have likely grown outside the prostate and may have spread to other parts of the body (such as the bones or lymph nodes). Once the cancer cells have grown out of the prostate and spread elsewhere in the body, the likelihood of complete cure is low. However, with the use of combined medications and treatment modalities, the cancer cells can be effectively managed to keep them controlled.
Treatment Options
The therapeutic options most suited for each patient will depend on a host of clinical parameters and are tailored for each patient. Our physicians work in collaboration with other physicians and support staff to create a comprehensive therapeutic plan.
Treatment options can include any combination of external beam radiation therapy, hormonal therapy and surgery (termed “multimodal therapy”) when the disease appears contained within the pelvis. When the disease appears to have spread beyond the pelvis to other organs, hormonal therapy is the mainstay to help delay progression of the cancer. After a certain amount of time, certain cancers no longer respond to hormonal blockade. Chemotherapy also has a role in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. There are multiple chemotherapy trials underway investigating the optimal treatment regimen to help manage these cancers.
Prostate Biopsies
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer among men after skin cancer. However, the disease can be extremely curable when diagnosed in the early stages. The urologists at Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles have access to the industry’s most cutting edge diagnostic and surgical tools. Whether obtaining a diagnosis for the first time or looking for a second opinion, men can get faster and more accurate results than ever before. With new imaging techniques and highly refined, minimally invasive procedures, cancer screenings and biopsies have come a long way in the last few decades, offering men higher survival rates and better quality of life.
Enhanced Prostate Imaging Techniques
MRI Fusion Biopsy
The board certified and award winning team of prostate cancer specialists at Comprehensive Urology uses an enhanced imaging and diagnostic technique known as MRI fusion biopsy. Because tumors are not always detectable on ultrasound exams alone, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) screenings can provide more detailed results.
An MRI fusion biopsy goes a step further than the regular test. It merges the images and data from an ultrasound and MRI screening to offer urologists a more precise, accurate view of the prostate and more specifically the size, location, and severity of the tumor.
Cancer Specialists in Los Angeles
The expert urologists at Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles are industry leaders in diagnosis and treatment. They operate on the philosophy that every patient is unique and one size does not fit all when it comes to treatment and care.
Patients can expect individualized, comprehensive exams and evaluations to determine the treatment plan most appropriate for their situation. Determining the right stage and grade of tumors is very important in devising an adequate treatment plan for each patient, and the state-of-the-art tools available at Comprehensive Urology help to yield clearer and more accurate results than ever before.
Robotic Prostate Cancer Surgery
In keeping with a career-long commitment to excellence, the team of experts at Comprehensive Urology offers the most advanced diagnostic and imaging capabilities for treatment in Beverly Hills. Recent advancements in medical technology have made it possible for the specialists and urologists at Comprehensive Urology to offer patients a range of minimally invasive, high precision treatment options in a state-of-the-art facility.
What is Robot Prostate Cancer Surgery?
Robot-assisted, or robotic, surgery allows the urology team at Comprehensive Urology to operate on patients with greater precision and flexibility than previously available with traditional “open” surgical methods. A computer guided system focuses on a targeted area of the prostate gland to remove tumors with greater accuracy. The “arms” of the robot are more flexible than human arms and can focus on a smaller and more targeted surface area, providing the surgeons with greater manual dexterity while performing surgery. Robotic surgery is a tool that works as an extension of the surgeon’s hand; they remain in control of the surgery and of the patient at all times.
Da Vinci Surgical System
The Da Vinci Surgical System is a revolutionary platform that allows Comprehensive Urology to offer patients minimally invasive, top of the line surgery for prostate cancer. The Da Vinci system is distinguished from earlier surgical tools and procedures with many unique features:
- Innovative EndoWrist instrumentation for greater manual dexterity and control
- High-resolution brilliant color 3D stereo viewer offers higher magnification to enhance natural depth of field
- Four robotic arms with jointed wrist design for greater dexterity and flexibility
- Motion scaling and tremor reduction of surgeon’s hand movements
- Multi-level fail-safe design to help minimize potential for human error
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery allows the experts at Comprehensive Urology to offer patients a less invasive, more precise operation. Minimally invasive surgery generally has many advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
- Smaller incisions
- Less blood loss
- More precise preservation of the erectile nerves
- More accurate urethral anastomosis
- Lower risk of complications and infections
- Potentially shorter hospital stays and healing time
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)

Treatment options have come a long way in the many years since the disease was first treated. However, the fight against the cancer has evolved at a far greater rate in only the last few years.
In addition to being able to catch the disease at an early stage in order to make it highly treatable, treatments have become exceedingly sophisticated. These countless advancements mean that patients have a better chance than ever to enjoy better post-operative health and preserve their quality of life.
Innovative new technologies and procedures for performing surgery and administering treatment to patients have made it possible for the urology team at Comprehensive Urology to treat all stages with more precision and success than ever before.
Treatment Options
While a cancer diagnosis can be frightening and overwhelming at any stage, men diagnosed with prostate cancer today have more treatment options than ever before. The experts at Comprehensive Urology work closely with each patient to accurately determine the stage and grade of the tumor(s) and to design an individual, customized treatment plan most appropriate for each particular case.
Traditionally, radiation treatments have been delivered to the entire prostate gland. The state-of-the-art facilities and equipment at Comprehensive Urology make it possible to offer each patient targeted and localized radiation treatments to the prostate gland in many cases.
MRI Truebeam Therapy
TrueBeam intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is a modern, highly sophisticated method for delivering targeted radiation treatments to the prostate gland with greater accuracy and precision. Because the positioning of the prostate gland tends to shift regularly due to its location near the bladder and rectum, older methods for administering radiation made it difficult to pinpoint the precise location of the gland. This increased the likelihood of applying radiation to healthy tissue as well. The enhanced imaging capabilities of the MRI Truebeam system make it possible to target and administer radiation to the cancer cells in the prostate with greater accuracy and precision.
IMRT typically takes eight and half weeks to deliver. Radiation is delivered in small fractions on a daily basis, Monday through Friday for 42 sessions. Each day that a patient shows up for his treatment, the prostate is in a slightly different position. This is because the prostate sits on top of the rectum and just below the bladder. Therefore, depending on the amount of fecal material in the rectum or the amount of urine in the bladder, the prostate can actually shift up or down slightly on a daily basis.
Standard IMRT radiation therapy cannot visualize the prostate with high accuracy. For this reason, to ensure that the prostate is being adequately radiated, some of the healthy tissue around the prostate also receives radiation. This is done to compensate for the lack of prostate visualization. The downside is that normal, healthy tissue gets destroyed with standard IMRT therapy.
MRI Brachytherapy
MRI Brachytherapy also utilizes the advancements in imaging and diagnostic capabilities that have occurred in recent years to help deliver precise, targeted radiation to the portion of the prostate gland where the cancer cells are located. This focus treatment helps preserve as much healthy tissue as possible and avoid over-treatment. With brachytherapy, the radiation doses are delivered through small capsules or “seeds” placed inside the patient near the location of the tumor.
FAQs

The team at Comprehensive Urology in Beverly Hills provides diagnostic capabilities and treatment options that are among the most sophisticated and effective in the country.
Patients from across the United States and even around the world seek out the practice’s industry-leading expertise and knowledge of the most advanced and cutting-edge treatments available for patients diagnosed with prostate cancer at any stage.
What are the signs and symptoms?
A: Like many forms of cancer, prostate cancer can sometimes be asymptomatic (presenting no obvious symptoms) in the early stages, when diagnosis and treatment has the highest likelihood of success. Knowing what to look out for and learning about personal risk factors should be a priority. Some of the most symptoms can include:
- Frequent need to urinate, especially at night
- Problems with starting urination or holding back urine
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Pain or burning during urination
- Difficulty with erection
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in urine or semen
- Frequent pain or stiffness in lower back, upper thighs, or hips
While the presence of any or a combination of symptoms does not necessarily indicate prostate cancer, men experiencing any symptoms should consult with an urologist as soon as possible.
When should I seek a second opinion?
It is never too late or too early to seek a second opinion.
What is the screening process?
The award winning team of specialists at Comprehensive Urology has the most advanced and reliable diagnostic imaging tools and equipment available. Screening and testing will vary from patient to patient, but diagnostic testing can include:
- Rectal Exam
- Blood Test
- Prostate Ultrasound
- MRI Fusion Biopsy
- Perfusion Dynamic MRI of the Prostate
Is this condition preventable?
While it may not be possible to predict or avoid the onset of cancer in all cases, there is no question that taking a proactive approach to nutrition and fitness, including a healthy diet and physically active lifestyle, can have a positive impact on overall health and well-being. Managing stress and anxiety is another important factor in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
What are the treatment options?
Every patient and diagnosis is different and therefore there is no “one size fits all” treatment approach. The expert urologists at Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles work with each patient to arrive at the best treatment plan available for every case on an individual basis.
How do I know what the best treatment option is for my case?
Every patient and diagnosis is different and therefore there is no “one size fits all” treatment approach. The expert urologists at Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles work with each patient to arrive at the best treatment plan available for every case on an individual basis.
What is the Prostate?
The prostate is an exocrine gland (glands that secrete outside the body e.g. prostate gland and sweat glands) of the male reproductive system and is located underneath the bladder.
What is the Prostate's Normal Function?
The prostate is comprised of thousands of tiny glands that produce fluid. This fluid forms part of the semen and primarily protects and nourished the sperm. When a male has an orgasm, the fluid is secreted into the urethra and leaves the body through the penis. The muscle fibers in the prostate gland also functions to control urine, or continence, by contracting and releasing the flow of urine through the urethra.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer normally starts in the gland cells, which is called adenocarcinoma. This type of cancer is considered to be a slow progressive disease that is not as easily detected compared to other forms of cancer. Prostate cancer starts with microscopic alterations in the shape and size of the prostate gland cells, which is referred to as Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN).
What Causes Prostate Cancer?
To this day, the specific causes of prostate cancer are still not certain. However, there are many contributing factors to the illness including age, ethnic background, lifestyle choices, medications, family history, and more.
- Age. The primary risk factor in developing prostate cancer is age. The risk is higher with age as there are more diagnoses of prostate cancer with men over the age of 50.
- Genetics. Family history also plays a major factor in prostate cancer risk. A man whose brother or father was diagnosed with the illness runs twice the risk of developing prostate cancer, compared to other men who do not have any affected family members.
- Diet. A few research studies have shown that certain diets, specifically a Mediterranean diet, may help reduce a person’s chanced of developing prostate cancer. Some recent studies promote the consumption of vegetables and vitamin B to be beneficial in prevention.
- Obesity. Those who are obese have been linked to an increased chance of developing cancer of the prostate.
- Other factors that increase the likelihood of developing cancer are linked to medication history and the contraction of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
How is Prostate Cancer Classified?
Classifying the right stage of cancer is extremely important. Not only will it help the doctor more clearly define the prognosis, it will help select the right form of therapy to use as well. The most common system for prostate cancer classification is summarized below:
- TNM (Tumor/Nodes/Metastases) is the most common system for determining the stage of prostate cancer used today. This system closely evaluates the size of the tumor, the number of lymph nodes and the presence of metastases.
- Computer tomography is used to determine if the prostate cancer has spread inside the pelvis.
- Bone scans are used to find out of the cancer has spread to the bones.
- Endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging can evaluate the prostatic capsule and seminal vesicles.
- The Gleason System, or score, is used to evaluate the biopsy samples under a microscope. If a pathologist detects cancer tissue, the tumor is then graded on a scale of 2 to 10. The higher the number, the more abnormal the tissues are compared to healthy prostate tissue. It is important to grade the tumor properly as it decides what treatments should be recommended.
What are the Signs and Symptoms?
As mentioned earlier, prostate cancer is not easily detected early on. Symptoms don’t normally appear during the early states, making it difficult for men to even they know they need treatment. Most men find out they have this condition after a routine check up or blood test. However, when symptoms do exist, they may involve one or more of the following:
- Frequent and sometimes painful urination
- Disruption in sleep due to more frequent urination at night
- Difficulty in starting and continuing to urinate
- Frequent and sometimes painful urination
- Disruption in sleep due to more frequent urination at night
- Difficulty in starting and continuing to urinate
What are the Symptoms Associated with Advanced Prostate Cancer?
The following are possible signs and symptoms of advanced state prostate cancer:
- Bone pain, most likely in the spine (vertebrae), pelvis or ribs
- Pain in the proximal part of the femur
- If the cancer has spread to the spine and is compressing the spinal cord, typical symptoms may include: leg weakness, urinary incontinence and fecal incontinence.
Contact a Specialist Today
It is crucial to receive a proper diagnosis in order to determine the best plan of care for those who have or think they may have prostate cancer. The skilled doctors at Comprehensive Urology in Los Angeles are leaders in their field. If you would like to receive a screening and biopsy or are interested in learning more about your treatment options, please contact us today at (310) 278-8330.
Learn more about prostate cancer treatment near me today.

Kia Michel, MD
Written by Dr. Kia Michel, a board certified urologist, surgeon, and founding member of Comprehensive Urology in Beverly Hills, Los Angeles. Dr. Michel's expertise includes focal therapy (HIFU/TULSA), prostate cancer treatment, robotic surgery, and male enhancement treatments such as Shockwave Therapy for ED and penile injections.
You must be logged in to post a comment.